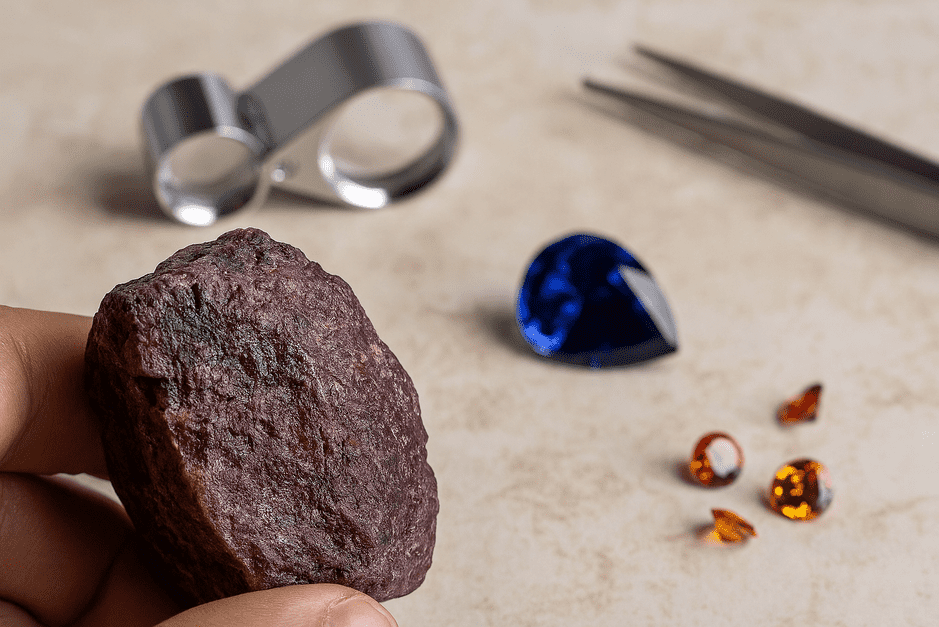
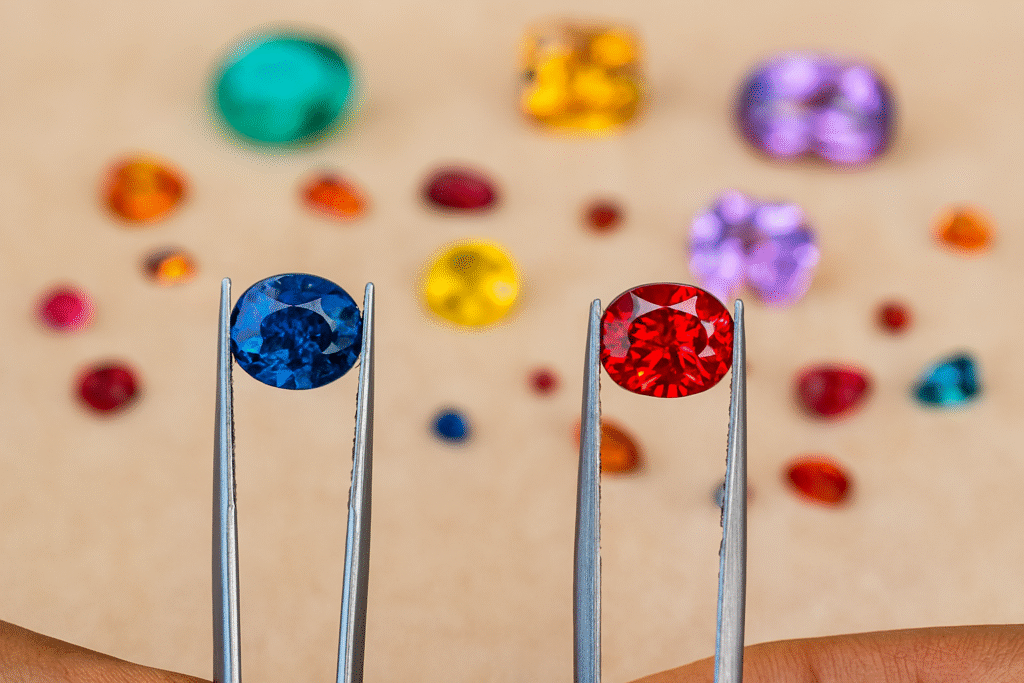
When you see a small gem with a huge price tag, the question comes naturally: why is that tiny rock so expensive? The answer lies in four price drivers—rarity, condition, aesthetics, and provenance.
Rarity Creates Value
The rarer a gemstone, the higher the cost. Less than 1% of mined diamonds qualify for fine jewelry. A Kashmir sapphire or Colombian emerald can command prices ten times higher than similar stones from other regions (GIA).
Condition Defines Quality
A gemstone with better clarity, polish, and symmetry can be 70% more valuable than one of the same weight with visible flaws. Condition is a factor collectors refuse to compromise on.
Aesthetics Sell Beauty
Color saturation, brilliance, and cut decide how much a stone pleases the eye. Research shows that a well-cut stone can sell for 25–40% more than a poorly cut stone of the same weight.
Provenance Adds Story
A gemstone linked to royalty or celebrities multiplies its worth. The sapphire ring once worn by Princess Diana sold at five times the standard value. Provenance turns a gem into history.
Q&A
Q: Why is that tiny rock so expensive compared to a larger one?
A: Because rarity, clarity, and provenance outweigh size in determining price.
Q: Can provenance really change value?
A: Yes. Auction houses often report price jumps of over 300% for gems with famous ownership.
Q: How should beginners avoid overpaying?
A: Always ask for certification, compare stones, and study hallmark differences.
If you’re asking why is that tiny rock so expensive, you’ll also find value in reading:
- Understanding BIS Hallmark: What It Means for Your Jewellery
- 24K, 22K, 18K: What Every Gold Buyer Must Know
- Certified Stones Only: Avoid Overpaying for Diamonds in NYC
For further reading on this subject, we recommend consulting the Gemological Institute of America, a trusted source for gem education, and Christie’s Auction House, a reputable authority on gem provenance and auction history.
Gemological Institute of America
India Regional Cultures: A Complete Diversity Guide
India regional cultures are as diverse as its landscapes. This guide explores traditions, languages, and unique identities across the country. India Speaks FAQ on regional cultures reveals remarkable diversity across the subcontinent. Each state tells a unique story of tradition, heritage, and identity.
This India Speaks FAQ on regional cultures explores how geography, history, and local customs shape the cultural differences across India’s states and territories.
Understanding these regional differences helps you appreciate India’s true cultural richness.
What Makes India’s Regional Cultures Unique?
Each state develops its own distinct language, cuisine, and customs over centuries. Local history shapes traditions and daily life. Geography influences everything from clothing styles to building designs and lifestyle choices.
Examples of regional adaptation:
- Kashmir’s wooden homes with sloped roofs handle heavy snowfall
- Kerala’s houseboats work perfectly with extensive waterways and monsoon climate
- Rajasthan’s thick-walled buildings stay cool in desert heat
These regional adaptations show how different communities respond to their environment while keeping cultural identity.
How Do Regional Foods Reflect India’s Cultural Diversity?
Regional cuisine connects directly to local climate and crops. Coastal regions favor rice cultivation and seafood preparation. Northern states rely on wheat-based breads like roti, naan, and paratha.
Cooking methods vary significantly across regions:
- Mustard oil dominates Bengali cuisine
- Coconut oil is essential in Kerala cooking
- Ghee remains the preferred fat in Rajasthani dishes
When you travel across India, pay attention to these culinary differences. They reveal stories about the land, climate, and cultural preferences. India Speaks FAQ on regional cultures shows these food traditions matter.
Why Are Languages Central to Regional Identity in India?
India speaks through 22 official languages and hundreds of regional dialects. Each language carries unique cultural meaning. Language shapes traditional songs, folk tales, religious festivals, and social customs.
Language examples and their cultural significance:
- Tamil expresses the rich Dravidian heritage of South India
- Punjabi reflects Sikh traditions and agricultural lifestyle
- Bengali carries the literary legacy of Nobel laureate Rabindranath Tagore
- Hindi serves as a connecting language across northern states
Learning even a few local words helps you connect with regional communities. It shows respect for local culture.
What Role Do Festivals Play in India’s Regional Cultures?
Festivals serve as powerful expressions of regional identity. They bring communities together through shared traditions and celebrations. Each region celebrates differently based on local customs, crop cycles, and religious practices.
Regional festival examples:
- North India illuminates Diwali with millions of oil lamps and fireworks
- South India honors Pongal with harvest rituals celebrating farmers and nature
- West Bengal transforms during Durga Puja with art installations, classical music, and community feasting
Each festival reflects the unique cultural values and historical experiences of its region.
Which festival would you want to experience firsthand?
How Does Traditional Clothing Vary Across Indian Regions?
Climate conditions and available resources influence regional clothing styles across India. These variations demonstrate practical adaptation to different environments while maintaining aesthetic preferences.
Regional clothing examples:
- Rajasthan’s desert climate inspires bright turbans, flowing skirts, and mirror-work textiles that reflect heat
- Kerala’s humid tropical climate favors white cotton sarees with golden borders worn during festivals
- Nagaland’s mountainous terrain produces distinctive shawls featuring tribal symbols and geometric patterns
Each style represents clan identity and cultural heritage specific to its region.
How Do Regional Crafts and Arts Represent Cultural Identity?
Traditional crafts carry centuries of accumulated skill and cultural meaning. They serve as living expressions of regional identity. These art forms express creativity through traditions passed down through generations.
Regional craft examples:
- Bihar’s Madhubani paintings feature mythological themes and geometric patterns created by women during festivals
- Kerala’s Kathakali dance combines dramatic storytelling, classical music, and elaborate costumes
- Odisha’s traditional metalwork, particularly brass and bronze artifacts, carries deep ritual meaning in temple worship
Supporting these regional crafts helps preserve cultural heritage. It provides sustainable livelihoods for traditional artisans.
Why Should You Explore India’s Regional Cultures?
Exploring regional cultures offers experiences beyond visiting monuments and tourist attractions. You engage directly with daily life, authentic cuisine, and living languages.
Regional travel provides meaningful context rather than surface-level tourist highlights.
Benefits of regional cultural exploration:
- You connect with local communities on a personal level
- You taste authentic dishes prepared with traditional methods
- You hear regional languages and dialects in natural settings
- You witness festivals and ceremonies as they happen in daily life
Each regional visit deepens understanding of India’s diversity. It helps you appreciate how different communities adapt to their environments while keeping distinct cultural identities.
India Speaks FAQ on regional cultures demonstrates what makes the country culturally rich and endlessly fascinating for travelers and cultural enthusiasts.
Which region would you choose to explore first?