Introduction
The integration of AI for Gem Grading is transforming the jewelry industry faster than any other technology in history. For centuries, the tools of the gemologist have remained unchanged: a loupe and a microscope. However, a seismic shift is underway. As a result, the industry increasingly relies on algorithms, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Machine Learning (ML) to enhance the speed, consistency, and accuracy of analysis.
Indeed, AI for Gem Grading is no longer science fiction; it is the industry standard in hubs like Surat and New York. By automating the assessment of the 4Cs (Color, Clarity, Cut, Carat), detecting treatments, and determining origin, AI-powered tools complement traditional analysis. Consequently, this shift helps reduce human subjectivity and expands capabilities through large data analysis. In this article, I will explore how these machines work, who the key players are, and whether a robot can truly replace a human gemologist.
AI for Gem Grading the 4Cs: Removing Bias
To begin with, the biggest advantage of AI is objectivity. A human grader can get tired, have eye strain, or have a bad day. A machine does not.
Color and Clarity
AI systems analyze high-resolution images and multi-spectral data to evaluate color. For instance, models utilize color spaces such as HSV to quantify hue, saturation, and tone. This enables more objective comparisons across stones, removing the “Human Error” of lighting conditions. In clarity grading, AI excels by highlighting microscopic blemishes that might be missed. Moreover, it instantly grades the overall transparency.
Cut Precision
Similarly, for Cut quality, algorithms measure proportions and facet symmetry. As a result, they assign a cut grade that mirrors industry standards with mathematical precision. Together, these automated assessments produce consistent results across different laboratories. You can read about traditional grading in my guide on Colored Stone Grading.
Detecting Treatments and Origins
Beyond simple grading, AI is revolutionizing the detective work of gemology.
The Origin Mystery
Determining where a stone came from (Provenance) is the hardest part of gemology. However, Machine Learning models are changing this. Algorithms like Random Forests are trained on expansive datasets that correlate gem features with geographic origin. Therefore, a machine can compare the chemical fingerprint of a Sapphire to thousands of samples from Kashmir, Sri Lanka, and Madagascar in seconds. This provenance inference supports accurate claims and combats misrepresentation.
Treatment Detection
Additionally, AI excels at detecting treatments. Technically, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) process images to identify subtle markers of heat treatment, irradiation, or diffusion. For example, it can spot the microscopic “fractured silk” in a heated ruby that a human might overlook. For more on treatments, check my Gemstone Buying Mistakes guide.
Industry Adoption of AI for Gem Grading
Several prominent labs and tech companies have embraced AI for Gem Grading.
- GIA (Gemological Institute of America): In collaboration with IBM, GIA leverages AI to classify Natural versus Laboratory-Grown diamonds. This partnership highlights how AI augments traditional workflows.
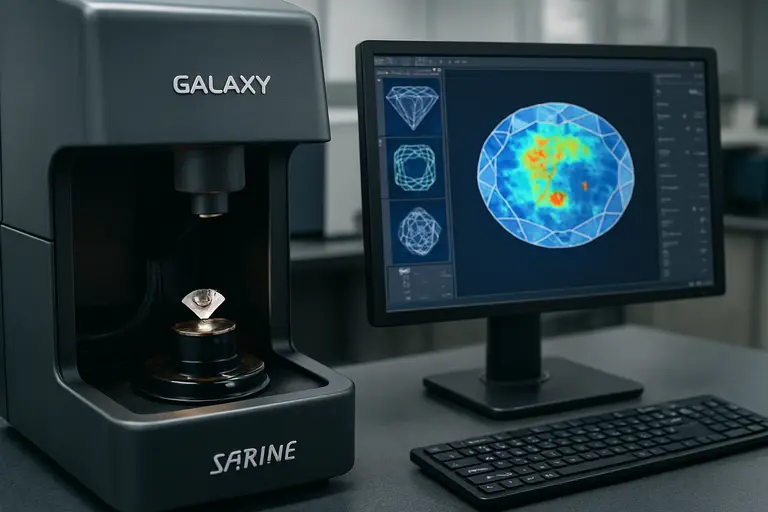
- Sarine Technologies: A pioneer in diamond technology widely used in India. Sarine uses AI for automated inclusion mapping (Sarine Clarity™) and light performance (Sarine Light™).
- Gübelin Gem Lab: The Swiss giants developed Gemtelligence. This AI system determines gemstone origin and detects treatments for colored stones like Rubies and Emeralds.
- De Beers: Employs automated machines (Falcon and Eagle systems) for high-volume grading.
These examples showcase how automated hardware, paired with AI analytics, can streamline large-scale operations. Read about how De Beers uses this for their ethical sourcing in my De Beers GemFair Artisanal Diamonds review.
Surat’s Role in AI for Gem Grading
Significantly, India is at the heart of this revolution. Surat, the diamond polishing capital of the world, relies heavily on AI. Before a rough diamond is cut, it is scanned by a Galaxy Machine. The AI maps every inclusion inside the rough stone and tells the cutter exactly how to cut it to get the maximum value. Consequently, this technology has increased the yield and profit of the Indian diamond industry by billions. Thus, for Indian jewelers, AI is not a luxury; it is a necessity for survival.
Benefits and Challenges of AI for Gem Grading
Despite the progress, the road ahead has hurdles.
The Benefits
- Speed: AI can grade hundreds of stones in the time it takes a human to grade one.
- Consistency: A machine in Mumbai will give the same grade as a machine in New York.
- Transparency: It reduces the likelihood of corruption or bribery in grading.
The Challenges
However, challenges remain.
- Data Quality: An AI is only as good as the data it is fed. If the dataset is biased, the grading will be biased.
- Nuance: Machines struggle with “Beauty.” A computer can measure color, but it cannot judge the “Romance” or “Velvet” of a Kashmir Sapphire vs Grandala.
Conclusion: Collaboration, Not Replacement
Ultimately, AI for Gem Grading is a tool, not a replacement. To maximize effectiveness, laboratories must integrate AI tools into existing workflows rather than replacing expert judgment. The future belongs to the “Bionic Gemologist”—a human expert armed with AI data. In summary, technology provides the data, but the human provides the wisdom.
FAQ: AI in Gemology
Do gemology and gem grading rely on AI?
Yes. Modern gemology increasingly uses AI to augment traditional grading. It is standard for large-scale diamond grading and is rapidly growing for colored stones.
Which gemstones are most affected by AI-based grading?
Diamonds are the most affected because they are standardized. However, AI is now being applied to Rubies, Sapphires, and Emeralds for origin determination.
Are AI grades accepted by reputable labs?
Yes. Labs like GIA, GCAL, and Gübelin use AI as part of their official grading process. It serves as a “Second Opinion” to verify the human grader.
How do AI systems detect treatments?
Fundamentally, they learn from massive datasets of images and spectral graphs. For instance, they can detect specific patterns in the crystal lattice that indicate High-Pressure High-Temperature (HPHT) treatment.
Where can I learn more about AI in gemology?
Consult the publications from major labs like GIA or technology partners like Sarine.
Author Bio
P.J. Joseph, also known as Saju Elizamma, Gemstone & Gold Consultant serving Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Karnataka.