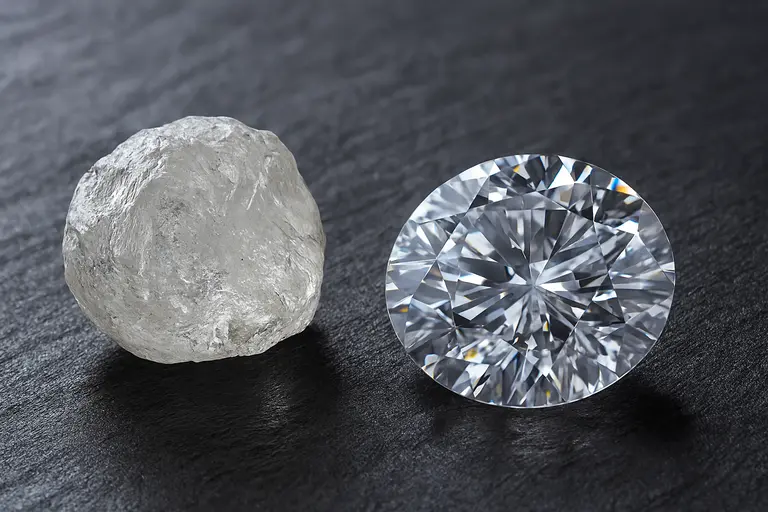
Introduction: Why Rough-Diamond Sales Changed Forever
In the latest Rapaport Diamond Podcast, Adam Schulman, founder and CEO of Koin International, explained how tenders and auctions reshaped rough-diamond sales. Before tenders became common, miners relied on informal, over-the-table deals. As a result, prices often stayed flat and buyers controlled the market.
During the conversation with Joshua Freedman, Schulman shared how competition improved transparency and why miners now prefer tenders. Because of these changes, auctions and tenders dominate the global trade today.
From Private Bags to Transparent Tenders
For decades, dealers bought rough diamonds in closed rooms, carrying bags of stones and making quick offers. While this approach worked for some, it lacked transparency. Therefore, Schulman saw a gap in the system.
- 2005: He co-founded Fusion Alternatives with I. Hennig. Since it was the first independent tender platform, it allowed small and mid-sized miners to reach more buyers.
- 2015: He launched Koin International to expand the model. After its success, tenders became the preferred sales method.
- Today, over 70% of rough diamonds are sold via tenders or auctions.
At the same time, De Beers and Alrosa continued their sight system. Yet miners shifted toward tenders because they could secure stronger competition and higher prices.
Learn more: How Diamond Auctions Work.
Q&A with Adam Schulman
Q: Why did tenders change the market?
A: Before tenders, miners often had no choice but to accept fixed offers. After tenders gained traction, they attracted hundreds of buyers and achieved 10–15% higher prices.
Q: Why did Koin relocate from Antwerp to Dubai?
A: “During Covid-19, Antwerp became difficult for global access. Meanwhile, Dubai offered lower tax, better logistics, and faster growth,” Schulman explained.
Q: Are tenders the new standard?
A: “Yes. Over time, tenders proved more transparent and competitive, so miners prefer them.”
The Business Impact of Tenders
Because miners wanted fair pricing, tenders delivered results. For example:
- In early Koin tenders, small miners gained 20% more revenue compared to direct deals.
- Dubai now accounts for 40% of global rough-diamond trade, proving its rise as a key hub.
- Koin hosts more than 20 tenders each year, drawing buyers from India, Belgium, Israel, and the UAE.
See also: Why Dubai Became a Diamond Hub.
Adam Schulman Beyond Diamonds
After years of building Koin, Schulman still finds time for his passion: photography. While leading diamond tenders, he also captures wildlife across deserts and safaris. His work appears on Instagram at @adam_s_photography.
For inspiration, explore Gemstone-Inspired Photography.
Adam Schulman, CEO of Koin International, joined the Rapaport Podcast to explain how tenders and auctions changed rough-diamond sales. From Antwerp to Dubai, the shift introduced transparency, competition, and better prices for miners. Today, auctions dominate because they bring more buyers and fairer results.
Suggested Reading:
Guide to Diamond Market Trends
History of Rough-Diamond Trading
This comprehensive global cuisine FAQ covers everything about Asian and Western food and drinks. Whether you’re exploring international cooking techniques or discovering new flavors, this global cuisine FAQ answers the most frequently asked questions about world food traditions, ingredients, and culinary practices from both Eastern and Western cultures.
Global Cuisine FAQ: Asian & Western Food & Drinks
Food reveals cultural contrasts in clear and delicious ways. From cooking methods to dining customs, Asian and Western cuisines showcase unique traditions while also offering fascinating overlaps. Below, you’ll find answers to the most common questions about these culinary worlds.
Understanding Core Differences in Cuisine
1. What distinguishes Asian and Western culinary traditions?
Asian meals often rely on rice or noodles as a foundation. Flavors usually come from soy sauce, ginger, garlic, and a wide variety of spices. Meanwhile, Western gastronomy emphasizes bread, potatoes, and pasta. Dairy plays a key role, with butter, cream, and cheese giving richness to many dishes. Herbs such as rosemary and thyme highlight European cooking. These contrasts create distinct dining habits and flavor profiles.
2. Are Asian dishes always spicy?
No, not at all. While cuisines from Thailand and parts of India feature bold use of chilies, not every dish follows this pattern. Japanese sushi, Chinese dim sum, and Korean bulgogi are mild examples. In fact, Asian cuisines range from fiery to delicate, showcasing a rich palette of flavor.
Western Breakfast Staples and Comfort Foods
1. What constitutes typical Western morning meals?
Western breakfasts often include eggs, bacon, and toast. Pancakes, waffles, and cereal are also popular choices. These hearty starts are usually enjoyed with coffee, tea, or juice, providing both energy and comfort.
2. What represents popular Western comfort foods?
Comfort foods in the West speak to nostalgia and indulgence. Creamy macaroni and cheese, pizza, and hearty casseroles are favorites. Similarly, burgers and fried chicken have wide appeal. Because they are warm, filling, and familiar, these dishes strongly connect to emotion.
Cultural Dining Practices
1. Do all Asian cultures employ chopsticks?
No. Chopsticks dominate in East Asia—China, Japan, and Korea. However, Southeast Asia prefers spoons and forks, while India and parts of the Middle East often use flatbreads or hands. This diversity highlights how food customs closely reflect culture.
2. Why are some Asian foods fermented?
Fermentation preserves food while also enhancing nutrition and flavor. Korean kimchi, Japanese miso, and Indonesian tempeh show how tradition meets health benefits. These foods are valued not only for taste but also for their role in well-being.
Common Western Beverages
1. What beverages are common with Western meals?
Western dining often features water, soda, or fresh juice. Alcohol also has a strong cultural connection, with wine served at European dinners and beer central in North America. In the southern United States, sweet iced tea is a staple.
Dietary Flexibility and Options
1. Can one discover plant-based options easily?
Yes. Asian cuisines offer tofu stir-fries, lentil dals, and vegetable curries that are naturally vegetarian. Western food, similarly, embraces plant-based eating. Salads, vegetarian pastas, and vegan burgers have grown popular, making meat-free dining accessible worldwide.
Unique Asian Drinks to Explore
1. What are some unique Asian beverages?
Asia provides a wide variety of distinctive drinks. Bubble tea, from Taiwan, combines tea with chewy tapioca pearls. Japanese sake, made from rice, holds deep cultural meaning. Strong Vietnamese iced coffee, sweetened with condensed milk, adds a bold twist compared to Western brews.
Portion Sizes and Dining Habits
1. How do portion sizes compare?
Western meals often emphasize large servings, reflecting abundance. By contrast, Asian meals are usually smaller yet balanced, encouraging sharing and mindful eating. This creates different social experiences around the table.
The Art of Fusion Cuisine
1. Is it feasible to integrate Asian and Western flavors?
Absolutely. Fusion cuisine blends traditions in creative ways. For instance, teriyaki burgers combine Japanese flavors with American fast food, while kimchi tacos bring Korean spice to Mexican street food. These playful mixes show how food bridges cultures.