Summary
GIA master stones are the diamond industry’s color grading standard. These carefully selected diamonds represent each grade from D to Z, ensuring accurate, consistent, and fraud-resistant color evaluation worldwide.
Introduction
When you buy a diamond, its color grade defines both beauty and value. But how do graders ensure consistency? The answer lies in GIA master stones — standardized reference diamonds used to maintain accurate color grading worldwide.
These calibrated stones create a universal benchmark. Whether in New York, Mumbai, or Antwerp, a GIA D-color diamond always matches the same standard.
Understanding GIA Master Stones
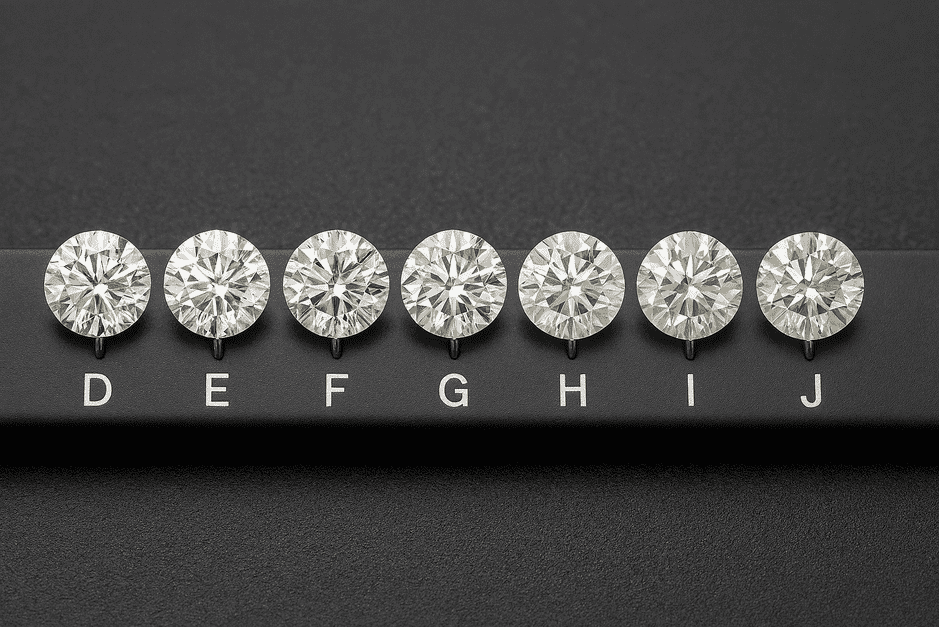
GIA master stones represent each grade on the D-to-Z color scale. Each one is a precisely selected round brilliant diamond that perfectly matches a specific color grade.
By using these stones, graders remove guesswork and achieve reliable results under controlled conditions.
Key features include:
- Exact match to assigned color grade
- Uniform cut and clarity
- Stable color over time
- Regular recalibration by GIA experts
How Gemologists Use Master Stones
Color grading requires strict lab conditions:
- Daylight-equivalent lighting
- Neutral gray backgrounds
- Controlled temperature and humidity
Gemologists place diamonds table-down next to master stones to see true body color. If a diamond falls between two grades, the lower grade is assigned to protect buyers.
Why GIA Master Stones Matter
1. Global Consistency
A G-color diamond in Los Angeles matches a G-color diamond in Bangkok. This ensures fairness and trust in every certificate.
2. Fraud Prevention
Standardized comparison blocks grade inflation. Sellers cannot exaggerate color grades without detection.
3. Buyer Confidence
When you buy a GIA-certified diamond, you know its color was verified using authentic master stones.
The D-to-Z Scale at a Glance
- D–F: Colorless
- G–J: Near colorless
- K–M: Faint tint visible
- N–R: Very light yellow or brown
- S–Z: Light yellow or brown
Practical Tips for Diamond Buyers
- Always check for GIA certification.
- Metal settings affect color appearance. Yellow gold can make faint tints appear whiter.
- Adjacent color grades often look similar in jewelry; differences are subtle.
Related posts:
The Future of Color Grading
New spectroscopic tools now complement traditional grading. These methods verify master stone comparisons and extend grading to fancy-colored gemstones.
The master stone system remains the foundation of reliable diamond color assessment, trusted globally by collectors and professionals.
FAQ
1. What are GIA master stones?
They are standardized reference diamonds used for accurate color grading.
2. Who uses them?
Only trained graders in accredited labs, primarily GIA.
3. Can buyers see them?
No. They remain in controlled lab environments to maintain accuracy.
4. Why are diamonds graded table-down?
Face-down viewing reveals the true body color without interference from sparkle.